Boxcar Scars: What They Are, Causes and Treatment Options
Are you looking for a way to make those boxcar scars less noticeable? Understanding the nature of these scars, their underlying causes and the treatment options available can help reduce their appearance. This article aims to provide comprehensive information on this skin condition and guide you towards suitable treatments.
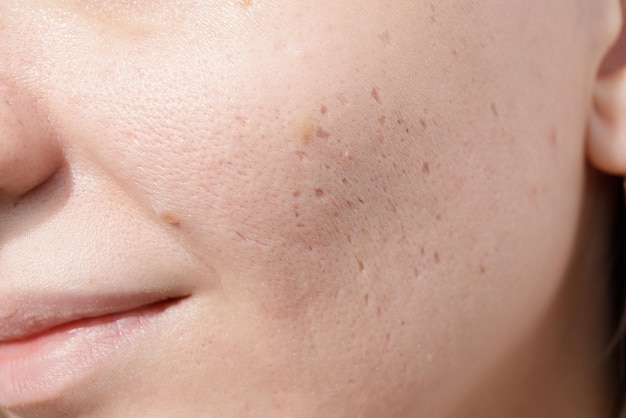
What are Boxcar Scars?
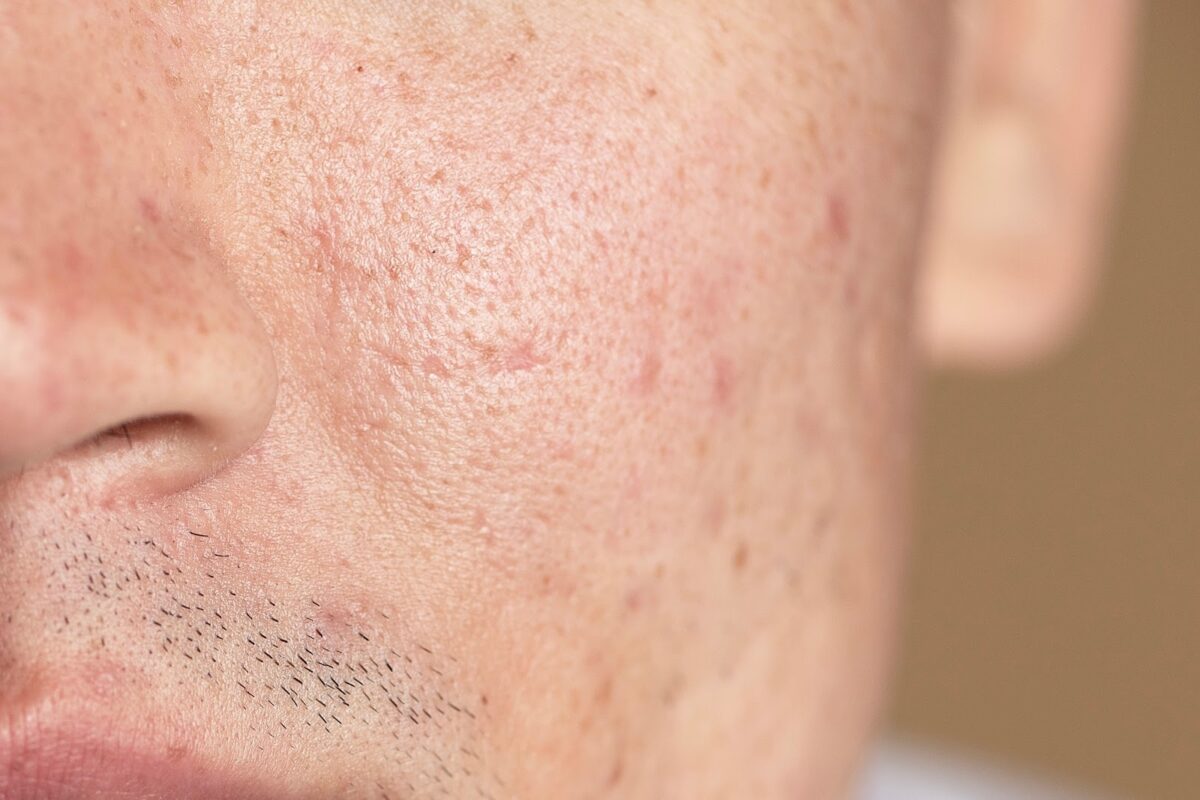
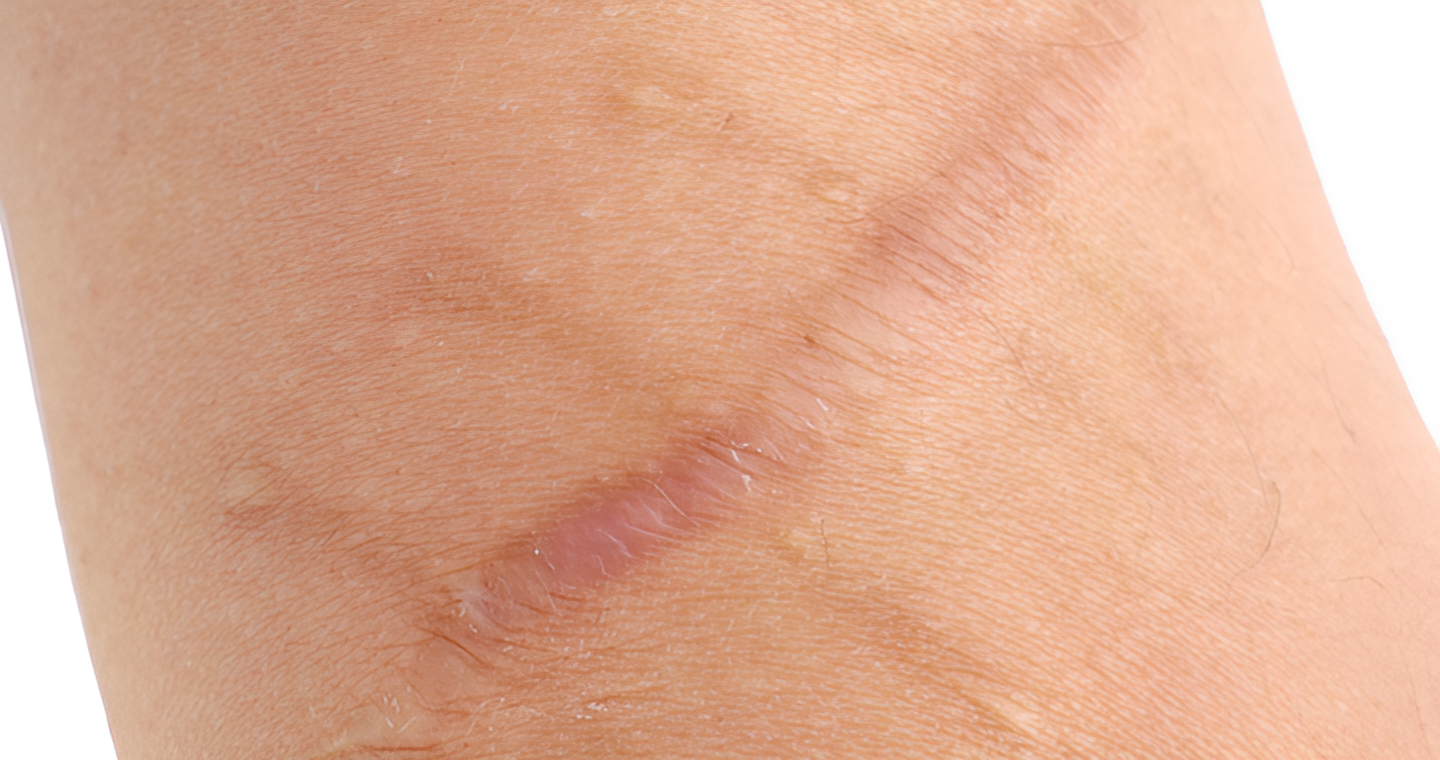
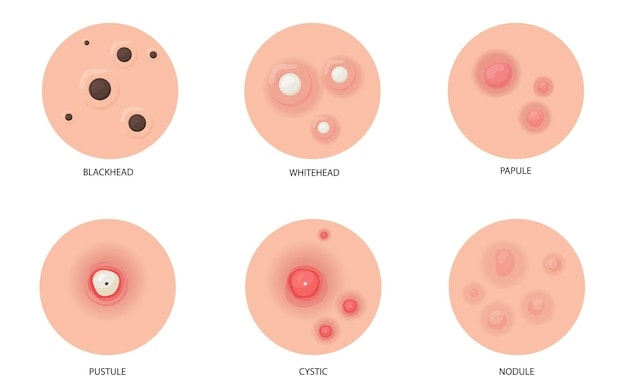
A boxcar scar is an atrophic scar characterised by broad, shallow depressions with well-defined edges. Unlike other atrophic acne scars, boxcar scars are usually oval or round. This gives the skin a pitted or uneven texture. Boxcar scars can vary in depth, with some being quite shallow and others more pronounced.
What Causes Boxcar Acne Scars?
The causes of boxcar scars primarily revolve around skin trauma and inflammatory conditions. Severe acne is the most common cause, particularly nodular or cystic acne.
How do boxcar scars form? When the skin is damaged, it typically produces collagen to aid skin repair. However, in the case of acne, the intense inflammatory response can cause the breaking down of collagen fibres within the dermis. As the skin heals, inadequate collagen production forms depressed areas on the skin’s surface.
Conditions like chickenpox and other skin damage can also contribute to how boxcar scars form, as they involve similar inflammatory processes that disrupt the skin’s structure.
Boxcar Scars vs. Other Acne Scars
Boxcar scars differ from other types of acne scars, like ice pick scars and rolling scars, in their appearance and formation. Here’s an overview of the differences between these types of scars.
| Type of Scar | Appearance | Description |
| Boxcar Scars | Broad, shallow depressions with well-defined edges | Boxcar scars can be shallow or deep. Deeper variants extend into the reticular dermis – the inner layer with connective tissues that support the skin. |
| Ice Pick Scars | Deep, narrow pits that extend into the dermis | It can penetrate deeply into the dermis, sometimes reaching the hypodermis |
| Rolling Scars | Wavy structure with sloping edge | They are shallower than ice pick and boxcar scars and have sloped edges due to tethering of the dermis to the underlying tissue. |
Treatment Options for Boxcar Scars
Treating boxcar scars involves a variety of options, each with its benefits and considerations. Multiple treatments may be recommended together, as each option can complement the others, potentially enhancing skin texture and appearance.
Surgical Method
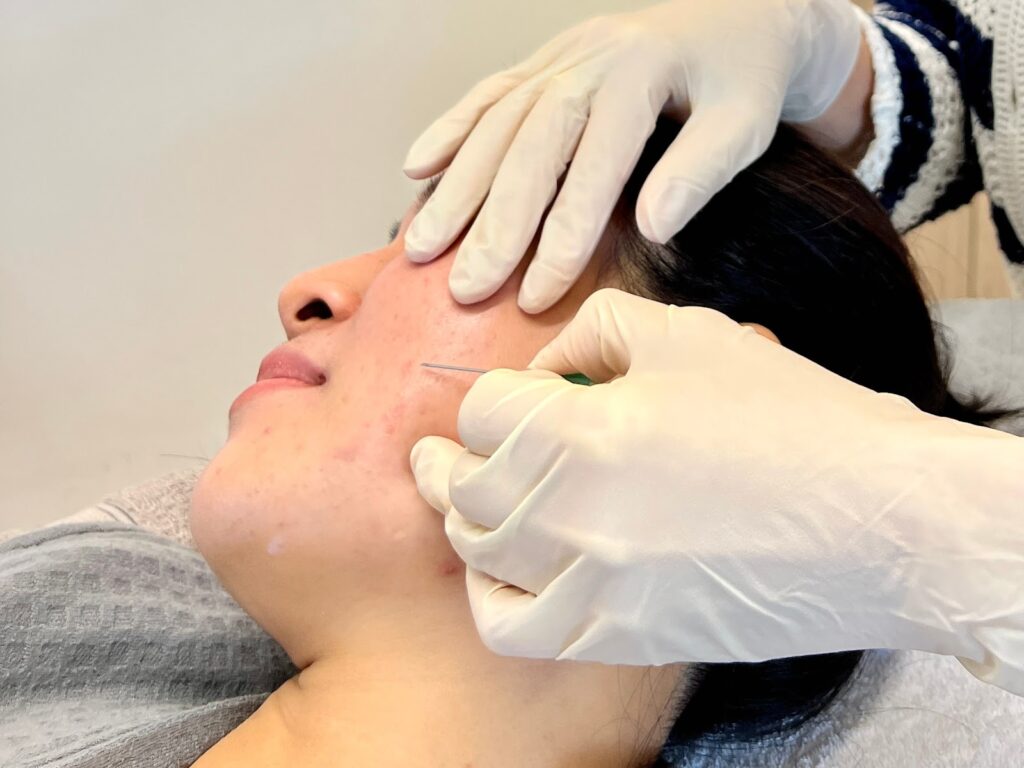
Surgical methods offer options for the treatment of boxcar scars. These approaches generally focus on removing or altering scar tissue to enhance skin texture and appearance.
Punch excision. This scar treatment involves excising the scarred tissue using a surgical punch. After the excision, the surrounding skin is stitched together. As the skin heals, new skin forms, creating a much smaller and less noticeable scar. This treatment can be used for deep boxcar scars.
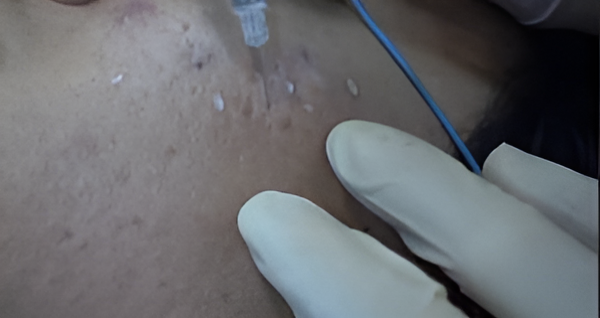
Subcision. Subcision is a minimally invasive procedure with a small needle inserted into the skin beneath the scar. The needle cuts the fibrous bands that tether the scar to the underlying skin tissue, lifting the scar. The mechanism relies on the body’s natural healing process, as new collagen formation occurs during recovery, gradually reducing the scar’s appearance and skin texture.
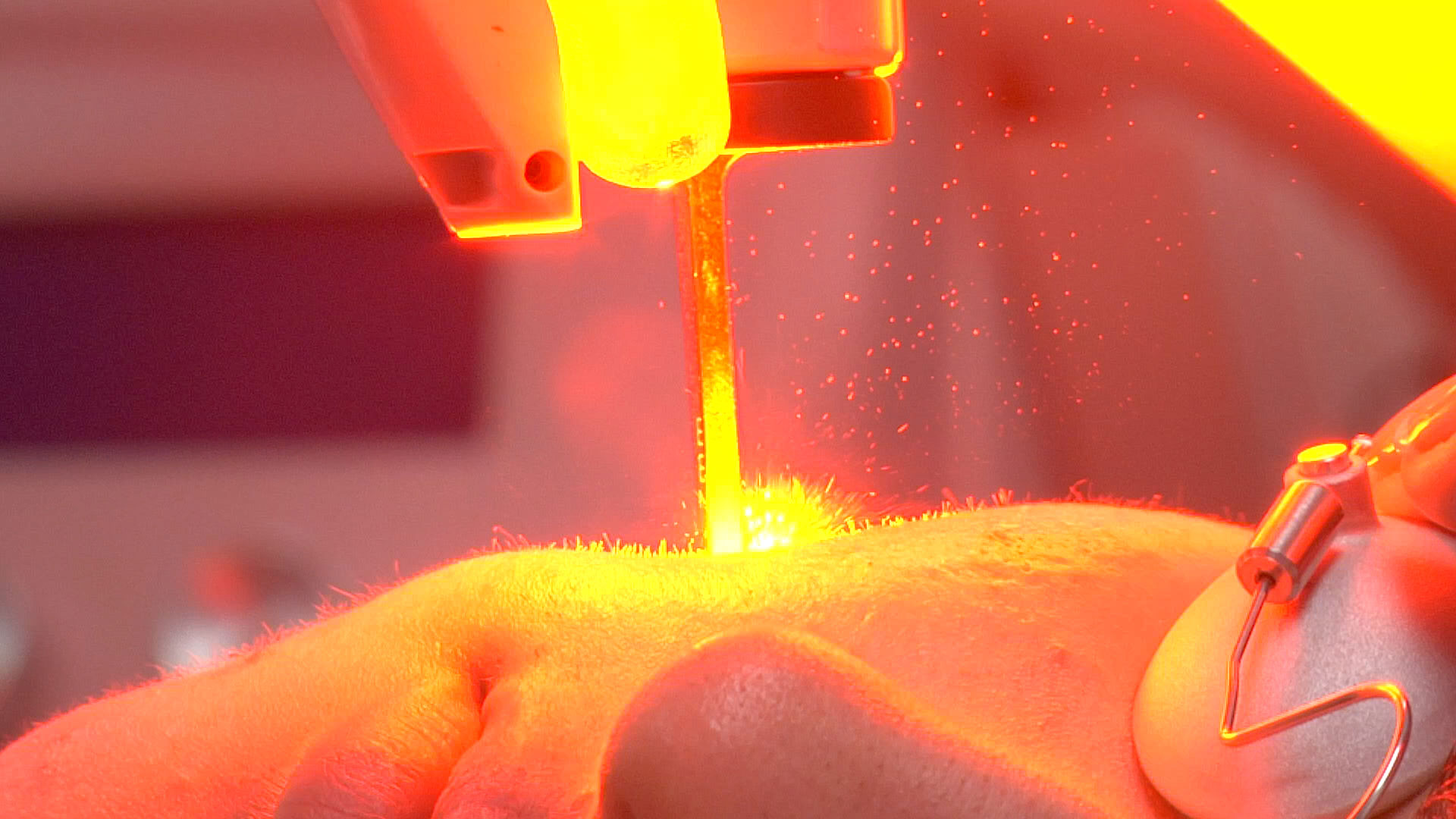
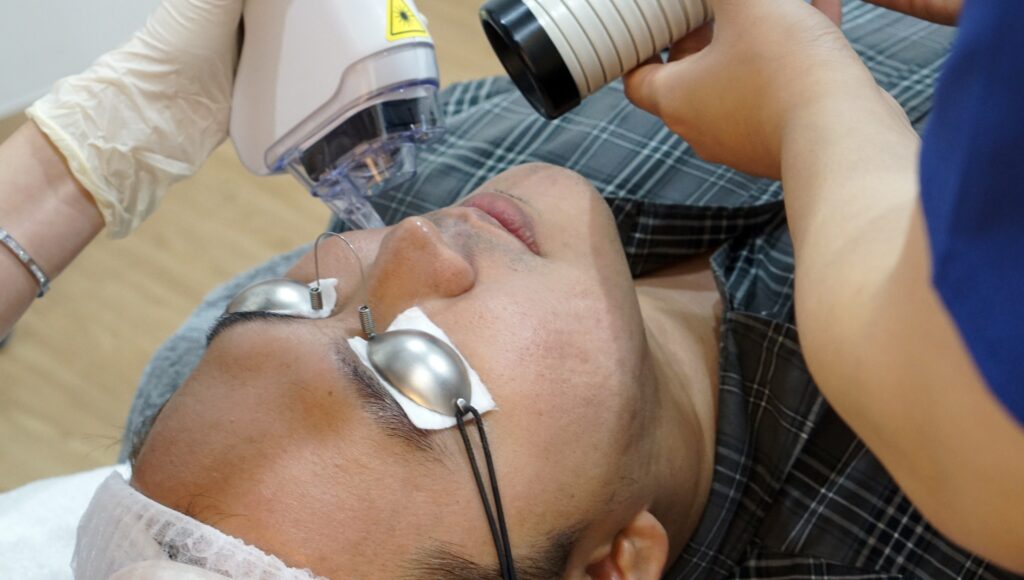
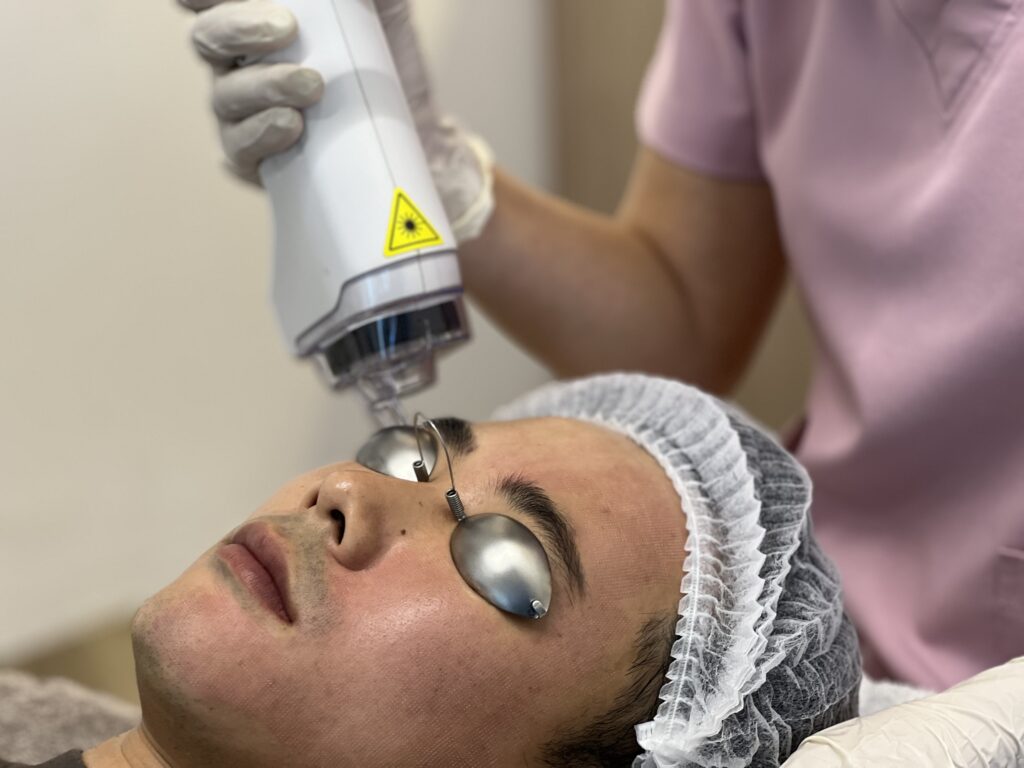
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy utilises beams of laser energy to target specific layers of the skin, promoting skin renewal and collagen production.
- Ablative laser therapy. It works by removing the outer layers of the skin, which encourages the body to heal and regenerate new skin. One of the most widely known ablative laser therapies used in aesthetic procedures is fractional CO2 laser. The mechanism involves emission of short-pulsed light energy that penetrates the skin, removing layers of scarred tissue and promoting new skin growth.
Microneedling
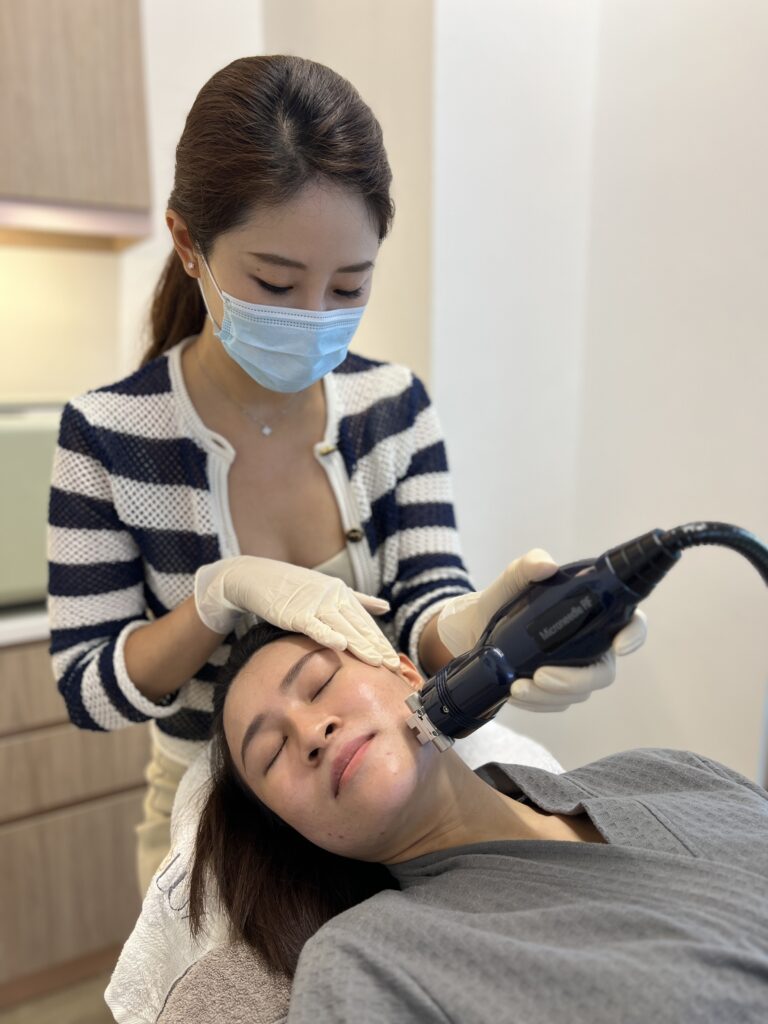
Microneedling, also called collagen induction therapy, is a treatment that involves stamping with fine needles to create controlled micropunctures in the skin. This stimulates the body’s natural healing process, resulting in increased collagen production, which improves skin texture and reduces the visibility of atrophic scars. At Lux Medical, we use a Radiofrequency Microneedling device to help further improve acne scarring. The microneedles give off radiofrequency at its tips to further stimulate collagen growth and help smoothen acne scars.
Chemical Peel
Chemical peels accelerate skin renewal by using chemical agents to remove damaged outer layers of skin. This triggers the body’s natural healing process, increasing collagen production. As new skin cells form, they can help fill in depressions caused by acne scars to reduce their visibility.
The common peeling agents are TCA , glycolic acid,. Different peeling agents come in different concentrations and are used depending on the penetration depth.
Dermal Fillers
Dermal fillers plump the skin from underneath, filling in the depressions caused by acne scars. When injected into the boxcar scars, fillers help to elevate the indented areas. Most fillers can provide quick and noticeable improvements in the appearance of boxcar scars.
The most commonly used fillers for this purpose include:
- Hyaluronic acid fillers. It provides immediate volume and can stimulate collagen production over time.
- Poly-L-lactic acid fillers. It works by stimulating collagen production to plump the skin gradually and reduce the appearance of scars.
How To Prevent Boxcar Acne Scars
Preventing boxcars and other acne scarring starts with early intervention, a proper skincare routine and proactive treatment strategies. With the right approach, it is possible to reduce breakouts, inflammation and reduce the risk of scarring.
1. Treat acne promptly
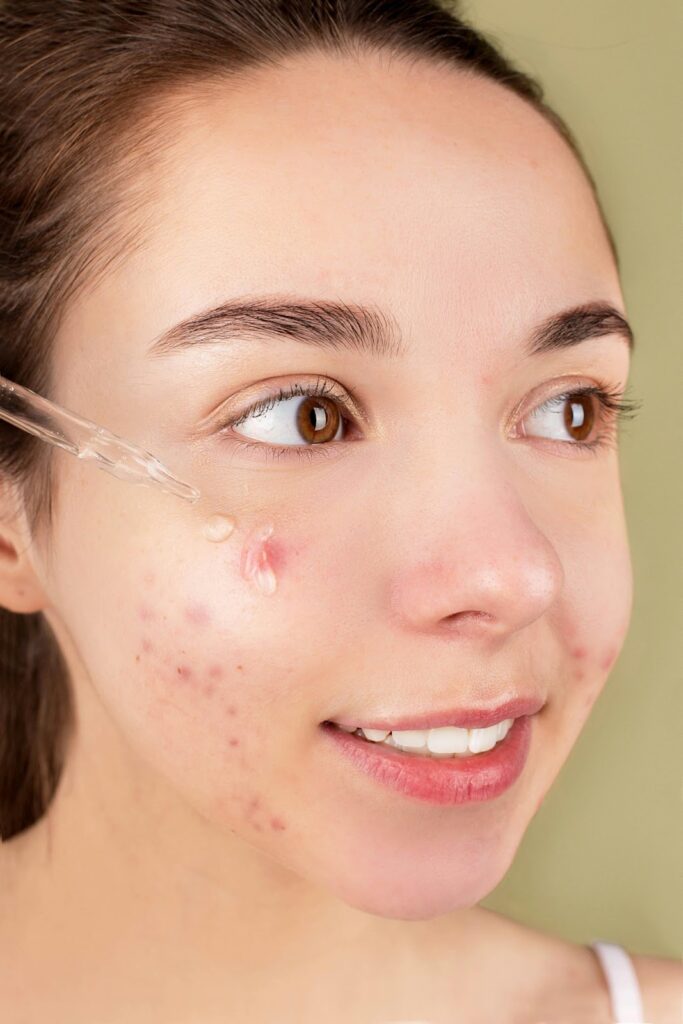
Addressing acne in its early stages is crucial to preventing long-term skin issues, including scarring. Timely treatment can help reduce inflammation and control breakouts.
Products containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can be effective for mild acne. However, it is essential to consult a skincare professional who can recommend appropriate treatments, including prescription medications or specialised therapies for more severe cases.
At Lux Aesthetic Clinic, we are dedicated to helping you manage acne and reduce the likelihood of scar formation. Schedule a consultation to start with a personalised journey towards clearer skin. – can be promotional since this is a blog
2. Opt for a gentle skincare routine
Look for cleansers, moisturisers and treatments without harsh chemicals, fragrances and alcohol, as these can exacerbate inflammation or disrupt the skin’s natural barrier. In addition, using non-comedogenic products designed not to clog pores can help prevent acne formation.
3. Hands off your face
Avoid picking or squeezing pimples, as it can worsen inflammation and increase the likelihood of scar formation. Touching your face can also cause the spread of bacteria and can irritate inflamed skin.
4. Use sun protection
Ultraviolet (UV) rays can delay the healing process by triggering inflammation, worsening scarring and existing acne. To minimise these effects, apply sunscreen consistently. Use a broad-spectrum oil free sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher and apply it repeatedly throughout the day.
5. Healthy lifestyle
A balanced diet of antioxidants and vitamins A, E and zinc can help prevent acne and support skin health. Staying hydrated helps maintain skin elasticity, while adequate sleep and stress management may help prevent acne breakouts.
Cost of Boxcar Treatment in Singapore
The cost of treating boxcar scars depends on various factors, like the type of treatment, the severity of the scars and the expertise of aesthetic professionals. Additionally, patients should consider the potential need for multiple sessions, which can impact overall costs.
We recommend scheduling a consultation with licensed dermatologists or aesthetic doctors to obtain detailed pricing estimates tailored to your needs and treatment plans.
Are boxcar scars permanent?
Boxcar scars are generally permanent, but their appearance can be reduced with various atrophic scar treatments. Consistent and targeted treatment can reduce the visibility of these scars over time.
Can boxcar scars be completely removed?
Removing boxcar scars completely is often challenging, especially for old and deep scars. While treatments can help manage their appearance, achieving a flawless, scar-free result is unlikely.
Treatment outcomes can include an improved skin texture and less noticeable scarring. It also depends on several factors, including the severity of the scars, the individual’s skin type and the chosen treatment method.
How long does it take to see results from treatments?
Improvements from treatment can vary depending on the treatment method and the severity of the scars.
- Immediate results. The results from dermal fillers are immediate, but they are temporary. They typically last from several months to a year, depending on the type of filler used.
- Gradual improvement. Laser therapy, Radiofrequency microneedling and chemical peels can help manage the appearance of scars over several weeks or months. Multiple sessions are often required.
Following the recommended treatment plan and aftercare instructions is essential for the best outcome. Treatment outcomes may also vary from person to person. Consult an aesthetic doctor to determine which treatment plan suits your specific concerns.
Conclusion
Boxcar scars can be a challenging skin concern. But with a clear understanding of their causes and available treatment options, you can make informed decisions to minimise their appearance and enhance overall skin health. While complete scar removal may not always be possible, various methods can achieve improvements.