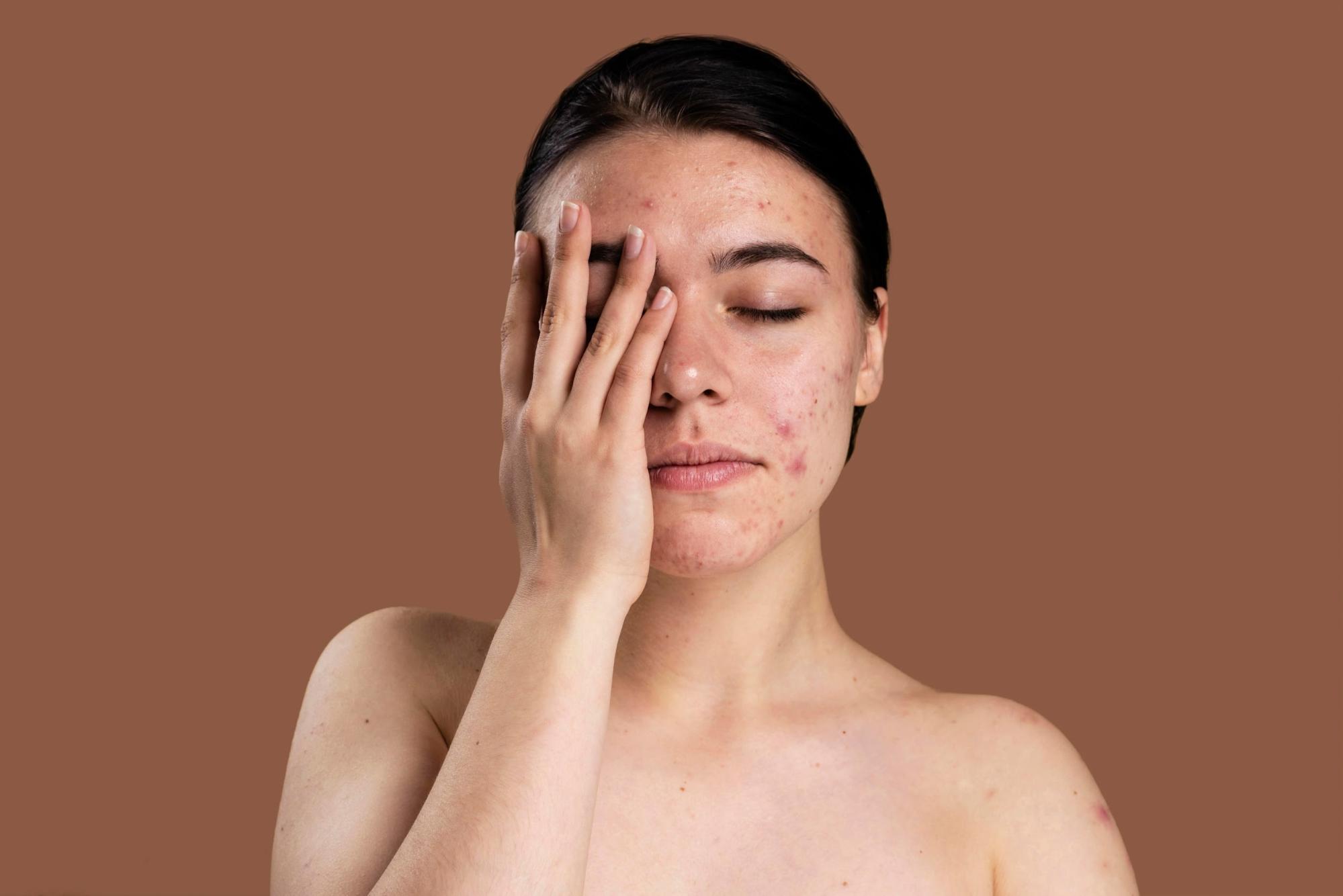
Acne is a common skin condition affecting millions of people worldwide, leading to various types of lesions. Among these, acne papules are a specific type of inflammatory acne lesion. Understanding acne papules, their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options can aid in managing the condition.
What are Acne Papules?
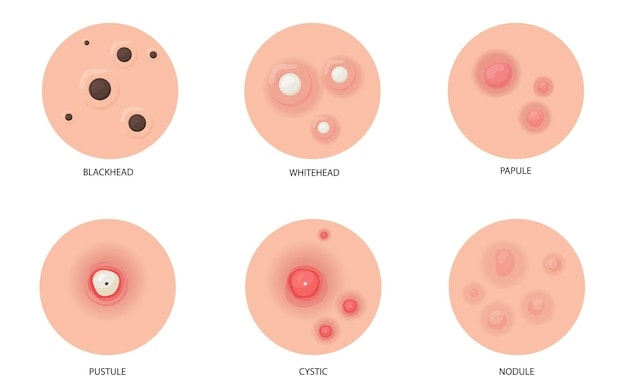
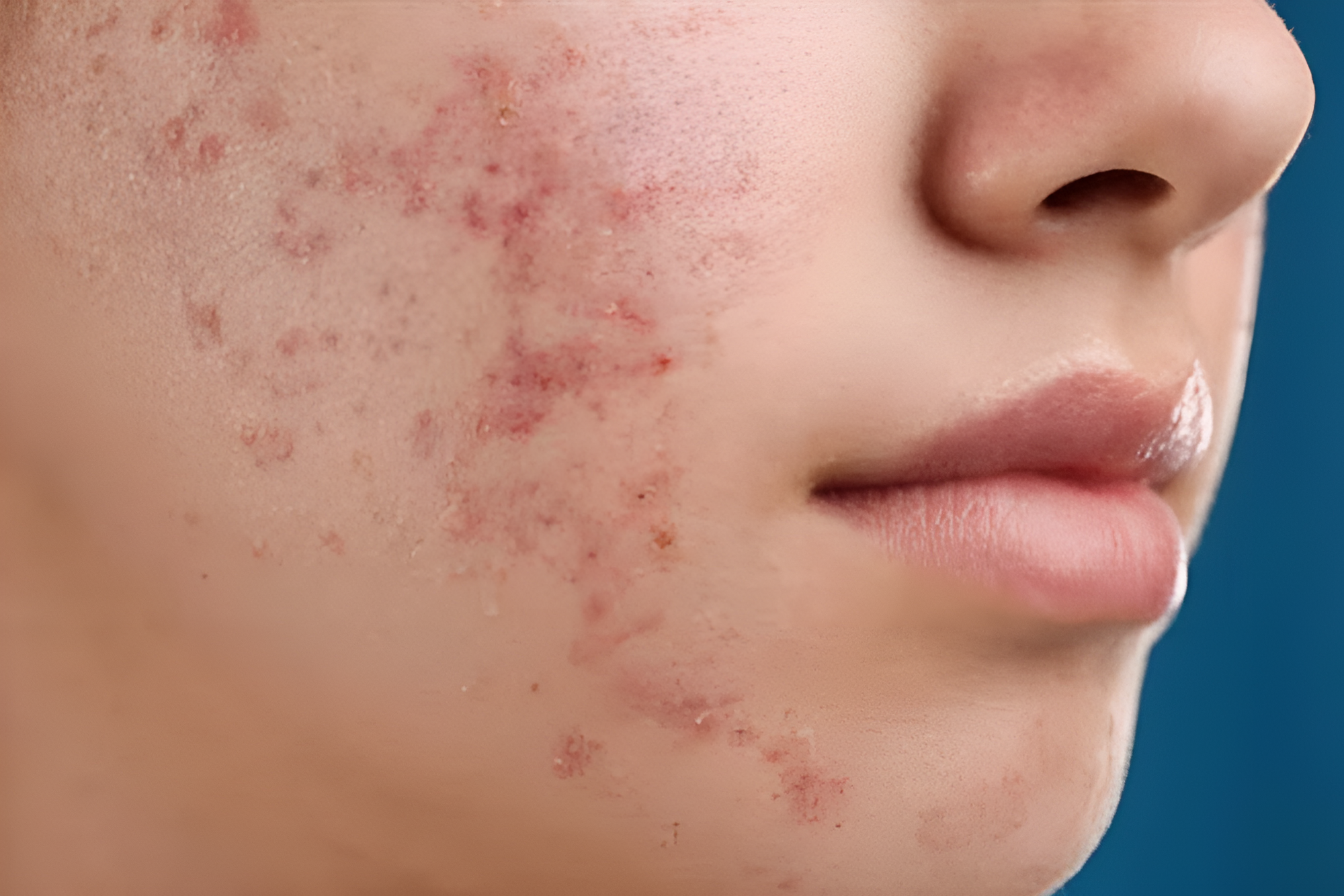
Acne papules are small, raised, reddish lesions occurring on the skin’s surface, typically less than 5mm in diameter. They are a type of inflammatory acne that forms when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Unlike pustules, papules do not contain visible pus. Papules are solid to the touch and often feel tender. If a papule fills with pus, it may develop into a pustule.
Acne papules are a form of inflammatory acne, distinct from other types of acne, such as whiteheads, blackheads, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
| Type of Acne | Description | Appearance | Common Locations | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whiteheads | Closed comedones filled with sebum and dead skin cells; not inflamed | Small, white or flesh-coloured bumps | Face, shoulders, back | Mild |
| Blackheads | Open comedones filled with oxidised sebum; not inflamed | Small, dark or black bumps | Face, shoulders, back | Mild |
| Papules | Inflamed, red, solid bumps without pus | Red base with a white or yellow centre | Face, back,chest, shoulders | Mild to Moderate |
| Pustules | Inflamed lesions filled with pus | Red base with a white or yellow centre | Face, back, chest , shoulders | Moderate |
| Nodules | Large, painful, solid bumps beneath the skin; deeply inflamed | Large, Hard,Red lumps | Face, Back, chest | Severe |
| Cysts | Deep, pus-filled lesions that are painful and can cause scarring | Face, back, chest | Severe |
What Causes Acne Papules ?
The development of acne papules is often attributed to several factors that contribute to skin inflammation and clogged pores:
Excess oil production
The sebaceous glands in the skin produce excess oil called sebum. This natural oil is essential for keeping the skin moisturised and protected. However excessive sebum production can combine with dead skin cells and debris, leading to clogged pores and the development of acne. This may result in blackheads, whiteheads, and more severe inflammatory lesions.
Maintaining a regular skincare routine and practising good hygiene may help manage sebum production and reduce the likelihood of clogged pores. Using gentle cleansers and avoiding harsh skincare products can also regulate sebum levels and keep pores clear.
Clogged pores
Dead skin cells that do not shed properly can mix with sebum, leading to clogged pores. This buildup can cause various skin issues, including acne, blackheads, and a dull complexion. Regular exfoliation and a proper skincare routine are essential for removing dead cells and maintaining healthy, clear skin.
Bacterial growth
The bacterium Cutibacterium acnes (formerly known as Propionibacterium acnes) thrives in clogged pores, contributing to inflammation. Although this bacterium is a normal part of the skin’s microbiome, excessive growth can trigger acne breakouts. Proper cleansing and the use of non-comedogenic products can help control bacterial growth and prevent pore blockages.
Inflammation
Clogged pores and bacterial growth lead to skin inflammation, which causes the formation of papules. These small, red bumps are often painful and can impact self-esteem. Regular exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and may reduce bacterial buildup and inflammation.
Additional factors, such as hormonal changes (during puberty or menstrual cycles), certain medications (like corticosteroids or lithium), stress, diet, and genetics, can also contribute to the development and worsening of acne papules by increasing sebum production and inflammation.
Symptoms of Acne Papules
Acne symptoms vary, but they typically include several common indicators. These can range from mild to moderate severity and may appear differently depending on the individual. Acne may appear anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on the face, chest, shoulders, and back.
Some common signs of acne papules include:
- Red or Pink Colouration: Papules are typically red or pink due to inflammation caused by the body’s immune response to bacteria and other irritants trapped in clogged pores.
- Inflammation and Tenderness: As a form of inflammatory acne, papules cause the surrounding skin to become red, swollen, and often tender to the touch.
- Absence of White or Yellow Pus: Unlike pustules, papules do not have a visible white or yellow head because the inflammation and blockage occur deeper within the skin, preventing the accumulation of pus near the surface.
- Progression Potential: Papules can sometimes evolve into more severe acne lesions. If they fill with pus, they may develop into pustules. In some cases, they can progress into nodules or cysts if the inflammation penetrates deeper into the skin.
- Duration: Papules may persist for several days to weeks, depending on their severity and the individual’s skincare regimen. While some heal on their own, others may take longer to resolve. It is advisable not to pick or pop a papule, as this can worsen inflammation and lead to scarring.
Common Areas Affected by Acne Papules
- Face: The forehead, cheeks, and chin are the most commonly affected areas.
- Chest and Back: Acne is prevalent in individuals who sweat excessively or wear tight clothing.
- Shoulders and Upper Arms: Though less common, these areas can be affected, often due to sweat and friction.
Diagnosing Acne Papules
Aesthetic practitioners diagnose acne papules primarily through a physical examination of the skin, assessing the severity and distribution of the lesions. During the consultation, additional inquiries may include:
- Acne symptoms
- Skin care routine and use of cosmetic products
- Medications currently being taken
- Allergic reactions to medications
- Hormonal fluctuations or menstrual cycle patterns (for women)
- Lifestyle factors, such as diet and stress levels
In rare cases, further tests may be required to rule out underlying conditions if acne presents suddenly and severely in adulthood.
Treatment Options for Acne Papules
If diagnosed with acne papules, treatment may involve a combination of topical and oral medications, as well as lifestyle changes. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalised treatment recommendations.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
For mild cases and severe forms of acne papules, several over-the-counter medications are available. These includes various topical treatments like:
1. Benzoyl peroxide
This OTC medication has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and keratolytic properties, helping to reduce bacterial growth and clear clogged pores by breaking down excess oil and removing dead skin cells.
It is commonly found in cleansers, spot treatments, and gels. Benzoyl peroxide can be drying or irritating, so it’s advisable to start with lower concentrations and increase gradually based on skin tolerance.
2. Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid penetrates deep into the pores to exfoliate the skin and remove dead skin cells, preventing clogged pores and reducing inflammation. Salicylic acid is available in various formulations, including cleansers, toners, and acne patches.
3. Azelaic acid
Naturally found in grains like barley, wheat, and rye, azelaic acid has both antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce swelling and kill bacteria on the skin, making it a useful treatment for mild to moderate acne papules. Azelaic acid is available in gels and creams, and it can be beneficial for those who find other treatments too irritating.
4. Retinoids
Topical retinoids, which are derivatives of vitamin A, help prevent clogged pores and promote cell turnover. They treat acne papules by reducing the formation of new lesions and decreasing inflammation. Retinoids are available both over-the-counter and by prescription. Prescription-strength retinoids, such as tretinoin, adapalene, and tazarotene, are typically more potent and used for more severe cases of acne.
Prescription Medications
For more severe or persistent acne papules, prescription medications may be necessary:
1. Topical antibiotics
These are commonly prescribed for moderate to severe acne papules to reduce bacterial growth and inflammation. Examples include clindamycin and erythromycin. These antibiotics are often combined with benzoyl peroxide to enhance their effectiveness and reduce the development of antibiotic resistance.
2. Oral Medications
For more persistent or severe cases of acne papules, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, and tetracycline may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and bacterial presence within the skin. They are generally used for a limited duration to prevent antibiotic resistance and are often combined with topical treatments for enhanced results.
3. Hormonal Treatments
Women with acne papules may benefit from hormonal treatments like birth control pills, which help regulate hormones that can contribute to acne. Oral contraceptives containing both oestrogen and progestin can reduce the activity of sebaceous glands, thereby decreasing oil production and preventing clogged pores.
4. Dapsone
A topical gel with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, dapsone is particularly effective for treating inflamed acne lesions like papules. It is usually applied twice daily and can be combined with other topical treatments for enhanced results.
Home remedies
While home remedies can be helpful for mild acne papules, their effectiveness varies, and they should be approached with caution due to potential irritation. Common suggestions include:
1. Tea Tree Oil
Known for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, tea tree oil can reduce acne-causing bacteria and inflammation. It should be diluted with a carrier oil before applying to the skin to prevent irritation.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial for treating acne. Applying aloe vera gel directly to the affected areas can help soothe the skin and reduce the appearance of papules.
3. Honey
Honey has antimicrobial properties and may help clear clogged pores. Applying a thin layer of raw honey and leaving it on for about 20 minutes before rinsing may provide soothing benefits.
4. Apple Cider Vinegar
Known for balancing the skin’s pH and its antibacterial properties, apple cider vinegar should be diluted with water before applying to the skin. Always perform a patch test first to check for skin sensitivity.
Medical Procedures
For individuals experiencing more severe or persistent acne, medical intervention may be necessary. Dermatologists offer a range of advanced treatments designed to address acne lesions and improve the overall appearance of the skin. These treatments target various aspects of acne formation, such as inflammation, bacterial growth, and clogged pores.
Before starting any new treatment, it is essential to consult with a dermatologist who can assess your skin type, acne severity, and overall health. They will provide personalised recommendations and guide you through an appropriate skincare regimen. In addition to medical treatments, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and proper sleep can support the skin’s healing process.
Acne treatment is often a gradual process, requiring patience and persistence. If one approach doesn’t yield immediate results, don’t be discouraged—clear skin often requires time and consistency.
Here are some of the common medical procedures used to treat acne papules:
1. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution, such as glycolic acid, to exfoliate the skin and remove damaged layers. This process helps to clear blackheads, whiteheads, and papules by unblocking pores and encouraging new skin growth. However, side effects may include temporary redness and increased sensitivity to sunlight, so it’s essential to follow your dermatologist’s aftercare instructions carefully.
2. Light and Laser Therapy
Light therapy utilises specific wavelengths of light to target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation. This treatment may help manage acne-causing bacteria and inflammation, potentially reducing the occurrence of papules. Various types of light, including red and blue light, may be used, and the procedure typically requires multiple sessions for optimal results.
3. Corticosteroid Injections
For large, painful papules or cystic acne, dermatologists may recommend corticosteroid injections. This procedure involves injecting a steroid solution directly into the affected area, which can reduce inflammation and the size of the lesion within a short period. It is often used for quick relief of severe breakouts that are resistant to topical treatments.
How To Prevent Acne Papules
Preventing acne papules involves several strategies to maintain skin health:
- Maintain a proper skincare routine: Use non-comedogenic products and cleanse the skin regularly to remove excess oil and debris.
- Avoid irritating products: Fragrance-free and gentle skin products are preferable.
- Manage stress: Stress reduction techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help reduce inflammatory responses.
- Dietary considerations: Avoid high glycemic foods that may trigger acne outbreaks.
When to Seek Professional Advice
While mild cases of acne papules can often be managed with OTC medications and lifestyle changes, more severe forms may require professional intervention. Consulting a medical or aesthetic practitioner can offer more targeted treatments and advice. Here are some indications that an acne papule might need medical attention:
- Persistent, severe acne papules that do not improve with OTC treatments
- Development of painful acne that causes discomfort
- Noticeable scarring or skin texture changes
- Emotional distress due to the appearance of acne
It’s also important to differentiate acne papules from other skin conditions like perioral dermatitis or keratosis pilaris, which may require different treatments.
For more information on professional treatments and personalised advice, you may consult a dermatologist or visit Lux Medical Aesthetic Clinic services page.
Conclusion
Acne papules, while common, can be effectively managed with the right knowledge and treatment approach. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can take control of their acne. While OTC medications and home remedies may help, seeking professional advice is often beneficial for more persistent or severe cases.