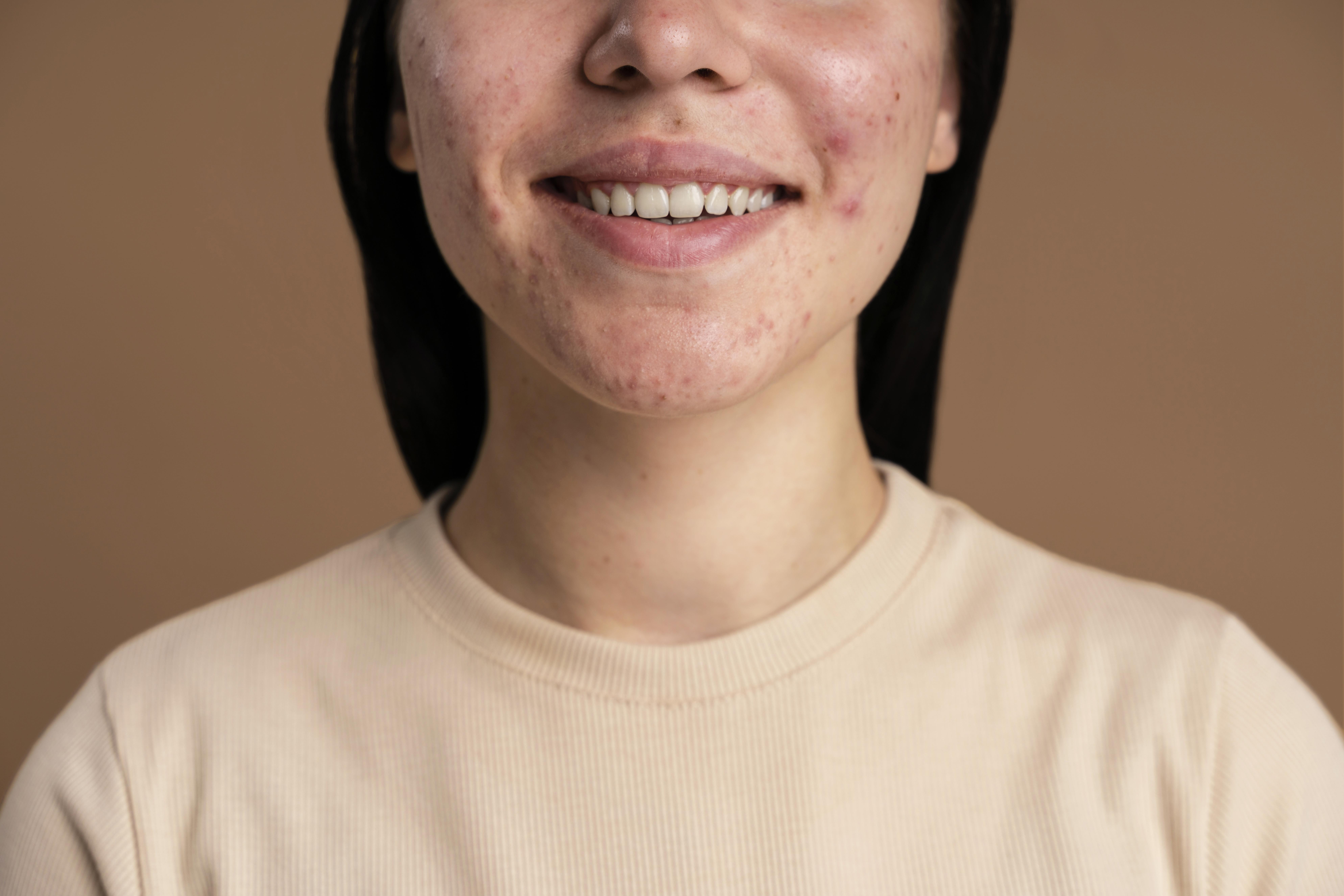
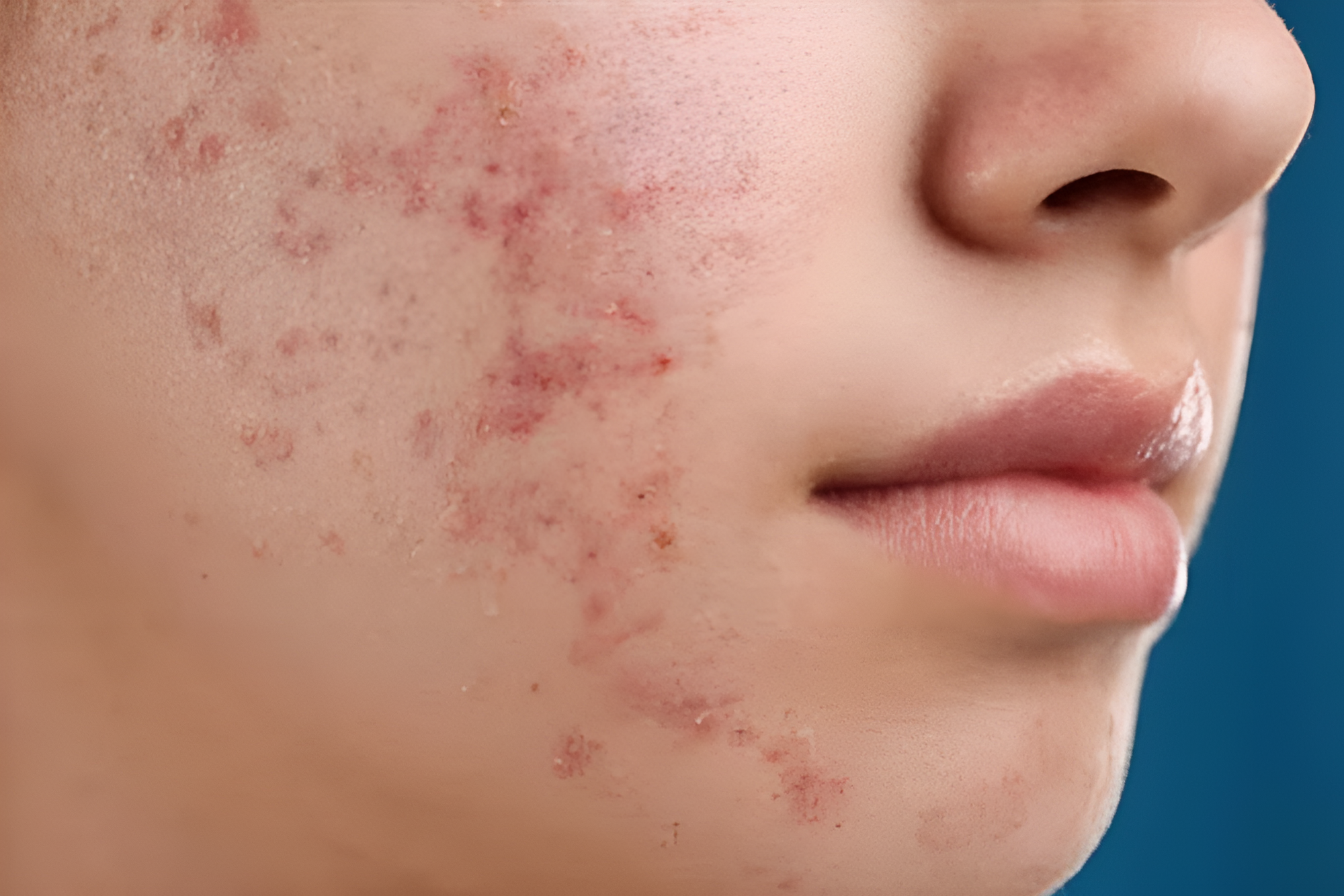
Hormonal acne often appears during periods of hormonal change. Unlike other types of acne, it’s closely tied to hormone levels, which can affect both how it develops and how it’s treated. Knowing what causes it, what symptoms to look out for, and when to seek professional care can help you better understand and manage your skin condition.
What is Hormonal Acne?
Hormonal acne occurs due to hormonal fluctuations involving androgens such as testosterone. These hormones can cause the oil glands, also known as sebaceous glands, to produce excess oil that clogs pores and leads to inflammation.
Hormonal acne is often characterised by deep, painful cysts that may not respond well to over-the-counter medications. Unlike other forms of acne, which may primarily be caused by bacteria or surface-level blockages, hormonal acne is primarily driven by internal factors, which may require a tailored management approach.
Causes of Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne tends to occur more frequently in women due to the cyclical nature of hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Several hormones and contributing factors are involved:
- Testosterone: Elevated testosterone levels can stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more oil, which may clog pores and lead to breakouts.
- Estrogen: Lower estrogen levels can result in a relative increase in testosterone, which may also contribute to acne.
- Other Factors: Stress, dietary habits, and lifestyle choices can influence hormone levels and potentially play a role in the development of acne
- Hormonal Imbalance: Fluctuations during the menstrual cycle may trigger acne flare-ups in some women. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome can also increase the likelihood of hormonal acne
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of acne may influence an individual’s tendency to develop hormonal acne.
Symptoms of Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne typically presents in a few specific ways that distinguish it from other types of acne:
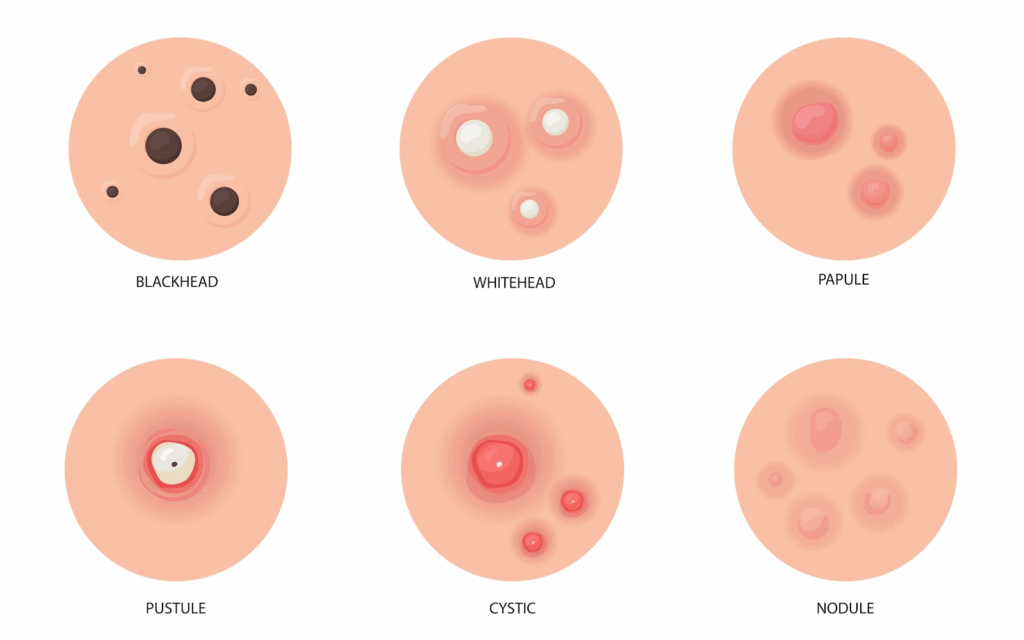
- Common Lesions:
Hormonal acne often leads to deeper, more painful breakouts, including inflammatory types such as cysts and nodules.- Comedones: These are clogged hair follicles (pores) that appear as blackheads or whiteheads.
- Nodules: Hard, painful lumps beneath the skin
- Pustules: Similar to papules but filled with pus
- Papules: Small, raised bumps that may be red and tender
- Cysts: Large, deep, painful, pus-filled lesions
- Common Areas Affected:
- Face: Particularly the lower cheeks, jawline, and chin.
- Chest: Hormonal acne can also appear on the chest, where the skin is prone to oil build-up.
- Back: The upper back is another common area for hormonal acne, often called “bacne”.
- Recurring Breakouts
- Hormonal acne tends to recur in the same areas due to consistent oil production patterns, often linked to hormonal cycles.
- Pain and Inflammation
- Lesions can be painful, tender, and inflamed, often causing discomfort and redness.
Understanding the hormonal triggers behind acne is crucial in determining the most effective ways to treat hormonal acne, whether through medication, topical treatments, or lifestyle adjustments.
Treatment Options for Hormonal Acne
Managing hormonal acne may involve a combination of over-the-counter treatments, prescription medications, natural remedies, and self-care techniques.
Understanding the various treatment options can guide your decisions about your skincare routine and indicate when it might be beneficial to seek professional advice, as individual results can vary.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments can help manage mild cases of hormonal acne, depending on individual skin types and conditions. These treatments often contain active ingredients that reduce oil production, unclog pores, and may help reduce the presence of bacteria associated with acne.
Common OTC products include
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Often used to reduce and prevent acne by helping to reduce bacteria and shed dead skin cells.
- Salicylic Acid: A beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) that exfoliates the skin and helps clear clogged pores while reducing inflammation.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): Ingredients like glycolic acid are used to exfoliate the skin.
- Sulfur: Used to dry the skin’s surface to absorb excess sebum and help unclog pores.
Prescription Medications
For more severe cases of hormonal acne, prescription medication might be recommended as part of the treatment plan. These can include both oral and topical medications:
- Topical Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, they work by normalising skin cell turnover, reducing inflammation, and helping to prevent clogged pores.
- Oral Contraceptives: Certain birth control pills may help regulate hormones, which can contribute to managing acne.
- Anti-androgen drugs: Spironolactone acts as an androgen receptor antagonist, helping to reduce the effects of androgens and lower sebum production.
- Oral Antibiotics: Often prescribed for their anti-inflammatory properties and to help manage bacteria on the skin.
Natural Remedies
While scientific research on the efficacy of natural remedies for hormonal acne is variable and often limited, some individuals report that these remedies complement their skincare routines as part of a holistic approach to managing their skin health. These remedies may include:
- Dietary Changes: Reducing dairy and high-glycaemic foods may help some individuals manage their acne.
- Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties that may help soothe the skin and support healing.
- Supplements: Some studies suggest that supplements such as zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics support general skin function.
Self-Care Techniques

In addition to medications, self-care practices can play a supportive role in managing hormonal acne. Here are some recommended practices:
- Cleansing: Use a gentle cleanser suited to your skin type to remove excess oil and dirt without drying your skin.
- Moisturising: Even oily skin needs moisture. Choose a non-comedogenic, oil-free moisturiser to keep the skin hydrated without clogging pores.
- Sun Protection: Wear sunscreen every day to shield your skin from the sun’s rays, which may irritate acne-prone skin and worsen post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Opt for a non-comedogenic sunscreen that’s less likely to clog pores.
- Avoid Picking: Refrain from picking or squeezing pimples to reduce the risk of inflammation and scarring.
- Stress Management: Try stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation, and ensure adequate sleep to help support hormone balance.
When to Seek Professional Advice
Consider consulting a qualified doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Your acne is severe, recurrent, itchy, or painful
- Over-the-counter treatments have not been effective after 2–3 months of consistent use
- You experience side effects from current medications
- You have underlying medical conditions, such as PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome).
A doctor can assess your condition, explore potential underlying causes, and recommend a suitable treatment plan.
At Lux Medical Clinic, our doctor is ready to assist you with a tailored approach to your skin concerns. For more information or to schedule a consultation, visit Lux Medical Clinic.
Conclusion
Managing hormonal acne can vary in difficulty depending on its link to hormonal fluctuations and individual skin characteristics. Understanding the causes and symptoms may help in exploring appropriate treatment options, such as over-the-counter products, prescription medications, or natural remedies. Incorporating self-care techniques and lifestyle changes can also support acne management.
If you’re struggling with persistent acne, consider consulting a medical professional to explore suitable options for your skin.
For more information on managing hormonal acne and exploring treatment options, consider scheduling a consultation with our professionals.