Blackheads are a common skin concern for many people, regardless of age or gender. It can be frustrating to deal with and may even impact one’s self-confidence.
This post offers an in-depth look into what blackheads are, their causes, their symptoms, and the various treatment options available. We’ll also provide practical advice on preventing blackheads from forming in the first place.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand how to manage and prevent blackheads.
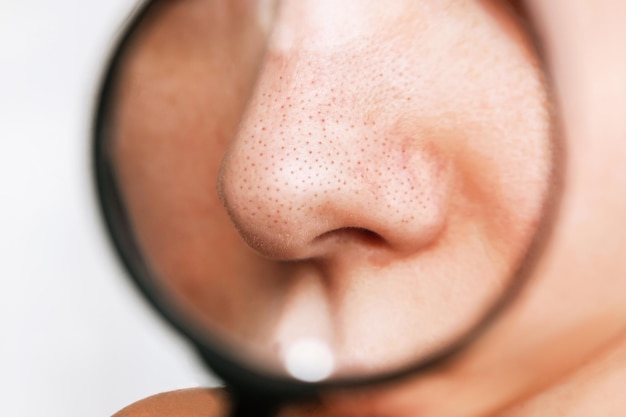
What are Blackheads?
Blackheads, also known as open comedones, are small, dark spots that appear on the skin’s surface. They form when:
- Oil and dead skin cells accumulate in the opening of a hair follicle
- The plug or clog becomes oxidised, turning dark when exposed to air
- The skin over the bump stays open, giving blackheads their characteristic black appearance
The black colour isn’t due to dirt but is a result of the oxidisation of the material trapped in the pore when it comes into contact with air.
Causes of Blackheads
Blackheads are primarily caused by a combination of factors that lead to clogged pores. Understanding these causes can help prevent and treat blackheads effectively.
Excess Oil Production (Sebum)
The skin’s sebaceous gland produces sebum (oil) to keep the skin hydrated. However, hormonal changes—such as those occurring during puberty, menstruation, or hormonal disorders—can lead to increased sebum production, contributing to blackhead formation.
Common factors that increase oil production include:
- Diet: High-glycemic foods and dairy products may trigger excess oil production.
- Stress: High stress levels can result in hormonal fluctuations, resulting in more oil.
- Humidity: High humidity can increase oiliness in the skin.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can stimulate oil production as a side effect.
Dead Skin Cell Accumulation
The skin naturally sheds dead skin cells, but when this process is disrupted, it can lead to a buildup that clogs pores. This accumulation, combined with excess oil, creates the perfect environment for blackheads to form.
Here’s a comparison of normal skin shedding vs. excessive dead skin accumulation:
| Skin Condition | Normal Skin Shedding | Excessive Dead Skin Accumulation |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Turnover Rate | Regular shedding every 28 days | Slower shedding, leading to buildup |
| Pore Appearance | Clear and unobstructed | Clogged and enlarged |
| Skin Texture | Smooth and even | Rough and uneven |
Genetics and Skin Types
Your genetics and skin type can also predispose you to blackheads. Oily skin, for instance, is more prone to blackhead formation, while some people naturally produce more sebum due to their genetic makeup.
| Skin Type | Susceptibility to Blackheads |
|---|---|
| Oily Skin | High |
| Dry Skin | Low |
| Combination Skin | Moderate |
Some genetic factors that can influence skin behaviour include:
- Family History: A tendency for acne or oily skin may run in families.
- Hormonal Sensitivity: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to react more strongly to hormonal changes, increasing oil production.
- Skin Texture: Genetic factors can affect how skin sheds dead cells and structures pores.
Symptoms and Appearance
Understanding blackheads’ appearance, common locations, and persistence can help aid in effective management and treatment.
Appearance of blackheads
Blackheads are typically characterised by:
- Size: They are small, often measuring 1-2 mm in diameter.
- Visibility: The dark centre is due to the oxidation of melanin when the clogged pore is exposed to air, not dirt.
- Texture: They are slightly raised but not inflamed or painful, distinguishing them from other types of acne, like pimples.
Quick Facts About Blackhead Appearance:
- Blackheads are open comedones, meaning the pore is open at the surface.
- They can appear on various skin types and are more noticeable on oily skin.
- Unlike whiteheads, which are closed comedones, blackheads do not have a white or yellow tip.
Locations of blackheads
Blackheads can appear on various parts of the body, though they are most commonly found on the face, particularly the nose, forehead, and chin. They can also appear on the back, neck, chest, and shoulders.
| Body Area | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Face | Very common |
| Back | Common |
| Chest | Less common |
Duration and Persistence
Blackheads may remain on the skin for an extended period if not addressed. Factors contributing to persistent blackheads include:
- Inadequate cleansing routines
- Use of comedogenic (pore-clogging) products
- Environmental pollutants
Treatment Options
How to remove blackheads? There are four common treatment options:
Over-the-counter treatments
For those looking to manage blackheads at home, over-the-counter (OTC) treatments can be effective. Skin products that contain salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide help exfoliate the skin and clear out pores.
- Salicylic Acid Cleanser: A gentle cleanser that penetrates pores to dissolve oil and dead skin.
- Benzoyl Peroxide Gel: A topical treatment that reduces bacteria and helps clear blackheads.
Prescription Medications
For more stubborn cases, prescription treatments like retinoids can be considered. Retinoids help speed up cell turnover, preventing the clogging of pores.
When to Consider Prescription Options:
- When OTC products are ineffective
- For severe or persistent blackheads
- When blackheads are part of a broader acne issue
Professional Treatments
Professional treatments like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and extractions are options that a qualified doctor can perform.
| Treatment Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Peels | Exfoliates skin deeply, removes dead cells | It may cause irritation, and multiple sessions may be needed |
| Microdermabrasion | Smooths skin texture, removes clogs | Multiple sessions may be needed |
| Manual Extractions | Immediate results | Risk of scarring if not done properly |
Preventing Blackheads
Individuals can minimise the occurrence of blackheads and maintain clearer skin by prevention. It includes effective skincare routines, lifestyle adjustments, and regular facial treatments.
Daily Skincare Routine

- Cleansing: Use a gentle, oil-free cleanser twice daily to remove excess oil and dead skin without over-drying the skin. Do this in the morning and evening.
- Exfoliation: Exfoliating skin can help remove dead skin cells that can clog pores. Look for skin products with AHAs or BHAs, such as salicylic acid. Do this once or twice a week.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose makeup and skincare products labelled as non-comedogenic (formulated not to clog pores).
Don’t forget to moisturise your skin and use sunscreen to protect skin from UV damage.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact blackhead formation. Key factors include:
- Diet: A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains may promote healthier skin.
- Stress: High stress levels can lead to hormonal changes that increase oil production, contributing to blackheads.
- Hydration: Drinking sufficient water helps maintain skin hydration and overall health.
Regular Facial Treatments
Regular facials, including extractions, can help prevent dead skin cells and sebum buildup that lead to blackheads. Opt for treatments that focus on deep cleansing and pore refinement.
| Facial Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Deep Cleansing Facial | Removes impurities, unclogs pores |
| Hydrating Facial | Balances oil production, hydrates skin |
Related Skin Conditions
Understanding blackheads in the context of other skin conditions provides a view of how different types of comedones and skin imperfections interact and can influence one another.
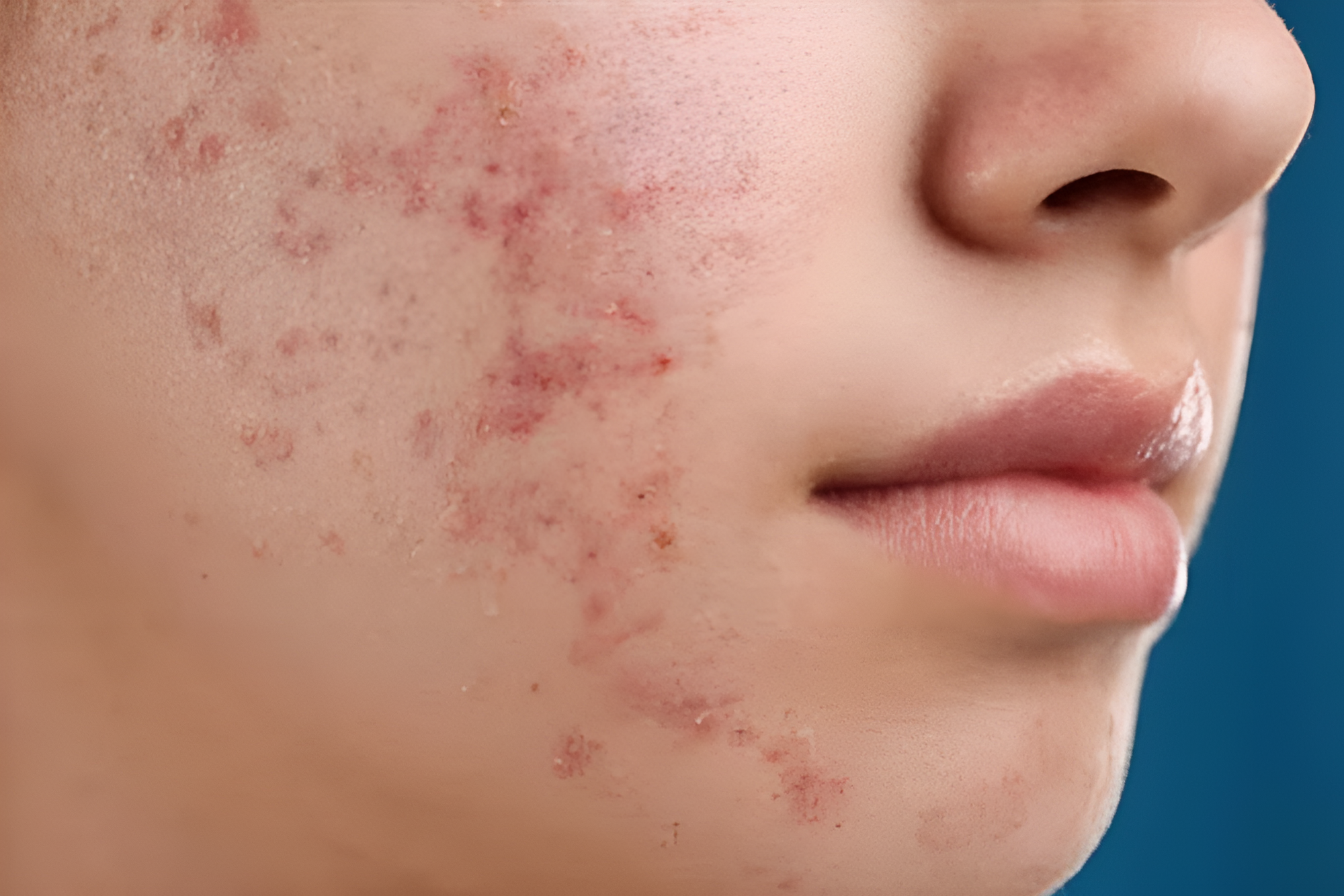
Acne and Other Comedones
Blackheads belong to a broader family of acne known as comedonal acne, which includes other forms like whiteheads and pustules. Whiteheads or closed comedones occur when these substances remain trapped beneath the skin’s surface, while pustules are inflamed lesions filled with pus.
| Type of Comedone | Appearance | Location | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blackheads | Open, darkened pore | Commonly on the face | OTC treatments, exfoliation |
| Whiteheads | Closed, white-tipped | Face, neck, shoulders | Topical treatments, extraction |
| Pustules | Red, swollen, painful | Anywhere on the body | Prescription medications, topical treatments |
Enlarged Pores
When the pores are clogged with oil and dead skin cells, they may appear larger and more visible on the skin’s surface. Regular exfoliation and pore-tightening treatments can help manage this issue.
Impact of Blackheads on Skin Health
While primarily seen as a cosmetic issue, blackheads can impact skin health and well-being.
How to Address the Emotional Impact of Blackheads:
- Seek professional skincare advice.
- Focus on holistic skin health rather than just appearance.
- Remember that blackheads are common and treatable.
Long-Term Skin Health
Untreated blackheads can lead to more significant skin issues, such as scarring or persistent acne. For long-term skin health, maintain a regular skincare routine.
| Long-term Consequences | Prevention Tips |
|---|---|
| Scarring | Avoid picking or squeezing blackheads |
| Persistent Acne | Use appropriate treatments early |
Myths and Misconceptions About Blackheads
Misinformation about blackheads can lead to ineffective skincare practices that potentially worsen the condition.
Pore Size and Blackheads
There are many myths surrounding pore size and blackhead removal. For instance, pore strips may offer temporary results but do not address the root cause of blackheads.
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Pore strips shrink pores | Pores don’t shrink but can appear smaller |
| Blackheads are caused by dirt | Blackheads result from oxidised oil and cells |
Conclusion
Blackheads are a common but manageable skin concern. By understanding them, from their causes to the treatment options, you can help prevent and treat blackheads effectively.
For persistent or recurring blackheads, consulting a doctor can provide tailored advice for your skin.